Electrochemistry | Class 12 CBSE Board Exam 2025
Key Concepts, Definitions, and Predicted Questions
Electrochemistry is one of the most important and scoring chapters in Class 12 Chemistry, especially for the CBSE Board exams. It deals with the study of chemical processes that involve the movement of electrons, particularly the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. This chapter also includes the study of electrochemical cells, galvanic cells, electrolytic cells, and the concept of electrode potentials, which have been frequently asked in previous board exams.
To excel in Electrochemistry for the CBSE 2025 board exams, it’s crucial to focus on fundamental concepts, key definitions, and formulas. Based on the analysis of past question papers and the importance of topics, the most likely questions that may appear in the upcoming exams are listed below. Emphasis is given to the weightage of marks and types of questions typically asked, like MCQs, short answers, and long answers.
Top 10 Important Topics from Electrochemistry for CBSE Board Exams 2025
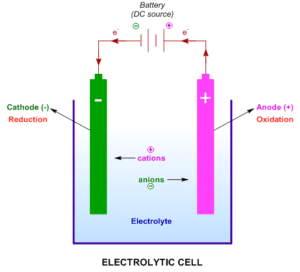
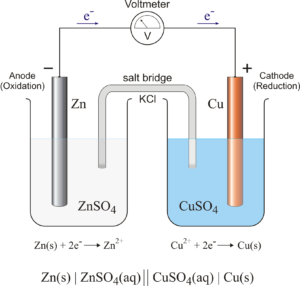
1. Electrochemical Cells (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells)
- Definition: A system that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- Formula: Cell potential (E⁰ cell) = E⁰ cathode – E⁰ anode
- Type of Questions: MCQs on cell components, short-answer questions on distinguishing between galvanic and electrolytic cells, and long-answer questions involving cell reactions.
- Predicted Question: Explain the working of a galvanic cell with a neat diagram, showing the flow of electrons.
2. Nernst Equation
- Definition: An equation used to calculate the cell potential of an electrochemical cell at any concentration other than standard state.
- Formula: E = E⁰ – (RT/nF) ln Q
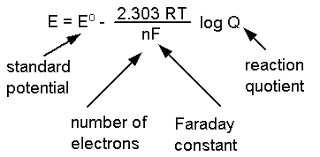
- Type of Questions: Short numerical problems based on calculating the EMF using the Nernst equation, derivation of the equation.
- Predicted Question: Derive the Nernst equation and calculate the EMF of a given cell.
3. Electrode Potential and Standard Electrode Potential
- Definition: Electrode potential is the potential difference between a metal and its solution, while the standard electrode potential is measured under standard conditions (1M, 1 atm, 298K).
- Formula: E° cell = E° cathode – E° anode
- Type of Questions: Definition-based questions, MCQs on electrode potentials of different electrodes, numericals using electrode potential values.
- Predicted Question: Define electrode potential. Calculate the cell potential of a given electrochemical cell using standard electrode potentials.
4. Conductance in Electrolytic Solutions
- Definition: Conductance is the measure of the ability of an electrolyte to conduct electricity.
- Formula: Conductance (G) = 1/Resistance (R)
- Type of Questions: Short answers on factors affecting conductance, numericals on calculating conductance, resistance, and molar conductivity.
- Predicted Question: Explain the concept of molar conductance and derive the relationship between conductance and molar conductivity.
5. Kohlrausch’s Law of Independent Migration of Ions
- Definition: The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the individual contributions of its cation and anion.
- Formula: Λ⁰m = Λ⁰+ + Λ⁰–
- Type of Questions: Derivations, numericals on calculating the molar conductivity at infinite dilution using Kohlrausch’s law.
- Predicted Question: State and explain Kohlrausch’s Law of independent migration of ions with an example.
6. Electrolysis and Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
- Definition: The process by which electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
- Formula: Faraday’s 1st law: m = ZIt
Faraday’s 2nd law: The mass of substances liberated is proportional to their equivalent weights. - Type of Questions: Short notes on Faraday’s laws, numericals based on the laws of electrolysis, electroplating.
- Predicted Question: Define Faraday’s laws of electrolysis. Calculate the mass of copper deposited when 0.5A current flows for 2 hours.
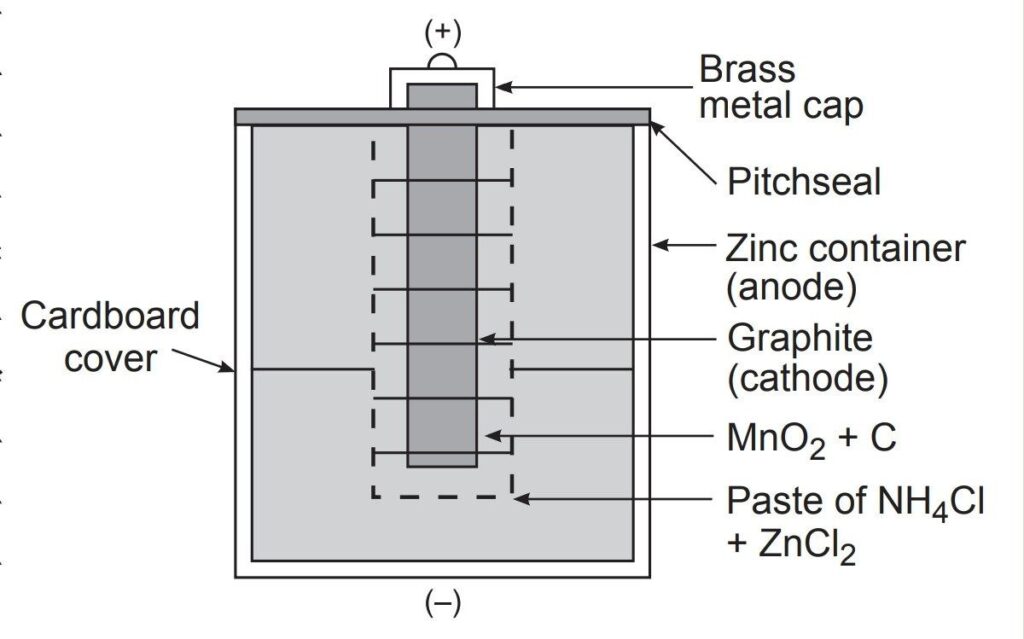
7. Batteries – Primary and Secondary Cells
- Definition: Primary cells cannot be recharged once used, while secondary cells can be recharged.
- Examples: Primary: Dry cell, mercury cell
Secondary: Lead-acid battery, lithium-ion battery - Type of Questions: Comparison of primary and secondary cells, working principle of lead-acid battery.
- Predicted Question: Differentiate between primary and secondary cells with examples.
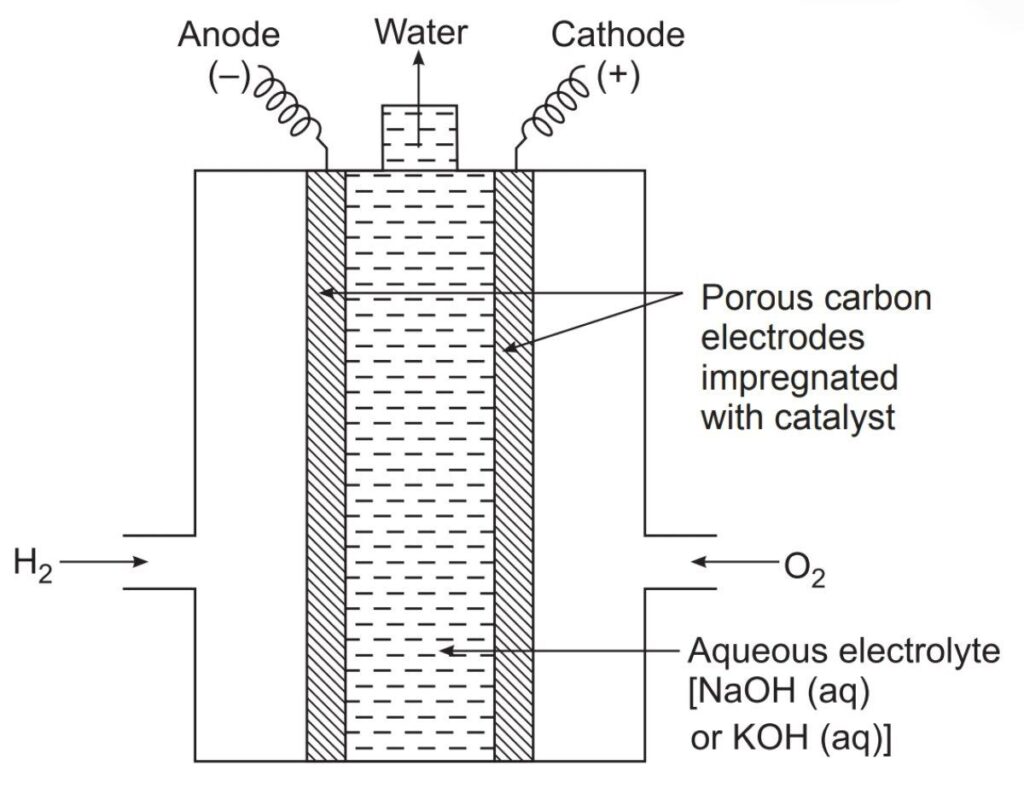
8. Fuel Cells
- Definition: A type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy from a fuel into electricity.
- Example: Hydrogen fuel cell
- Type of Questions: Short-answer questions on working principles, applications, and advantages of fuel cells.
- Predicted Question: Explain the working of a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell.
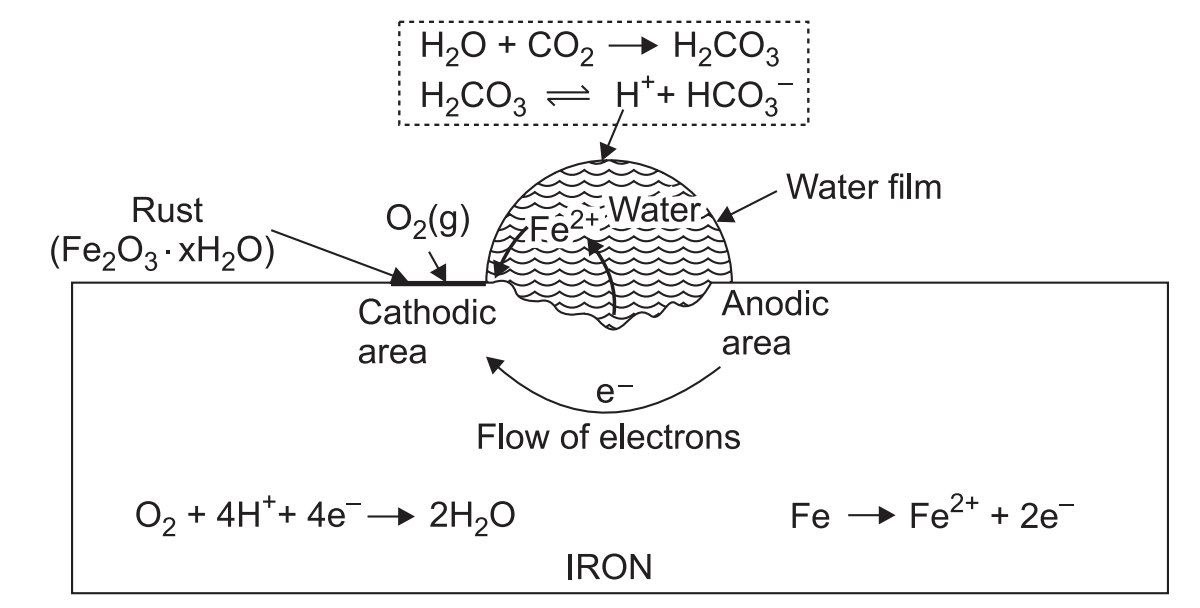
9. Corrosion and Its Prevention
- Definition: Corrosion is the gradual deterioration of metals due to electrochemical reactions.
- Type of Questions: Long-answer questions on methods of preventing corrosion, types of corrosion.
- Predicted Question: What is corrosion? Explain two methods to prevent corrosion.
10. Gibbs Free Energy and Cell Potential
- Definition: The change in Gibbs free energy determines the spontaneity of a reaction.
- Formula: ΔG = -nFEcell
- Type of Questions: Numerical problems on calculating ΔG, derivation of relationship between Gibbs free energy and cell potential.
- Predicted Question: Derive the relation between Gibbs free energy and cell potential and explain the significance.
Conclusion
Electrochemistry is a high-weightage chapter that requires clear understanding of fundamental concepts like electrochemical cells, electrode potentials, and electrolysis. Questions in the CBSE 2025 board exams are expected to focus on both theoretical explanations and numerical problems. Therefore, it is crucial to have strong command over formulas like the Nernst equation, Kohlrausch’s law, and Faraday’s laws. Pay special attention to previous year trends and practice numerical problems regularly.
Important Points to Remember:
- Understand the differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells.
- Practice numericals based on the Nernst equation, Faraday’s laws, and conductance.
- Focus on conceptual clarity in electrode potentials, Gibbs free energy, and corrosion.
- Diagrams and derivations (e.g., Nernst equation) are often favored in long-answer questions.
By mastering these concepts, students can confidently approach the Electrochemistry section in their board exams, ensuring a high score.
To enhance your preparation even further for CBSE 2025 Exam, you can also connect with us on YouTube, where we will guide you through all these topics in a comprehensive manner. To join us on YouTube, simply click the link below, and you’ve already taken your first step towards scoring better marks.
In the next post, we will discuss the key topics of the chapter ‘Chemical Kinetics.’
Note: All the topics covered in this article are based on the “Electrochemistry” chapter of Class 12 CBSE Board Chemistry and have been curated after analyzing previous years question papers. This article can be helpful for students aiming for success in exams, but it’s also important to thoroughly understand the entire syllabus and practice regularly.
Thank you!
Best wishes to all students!